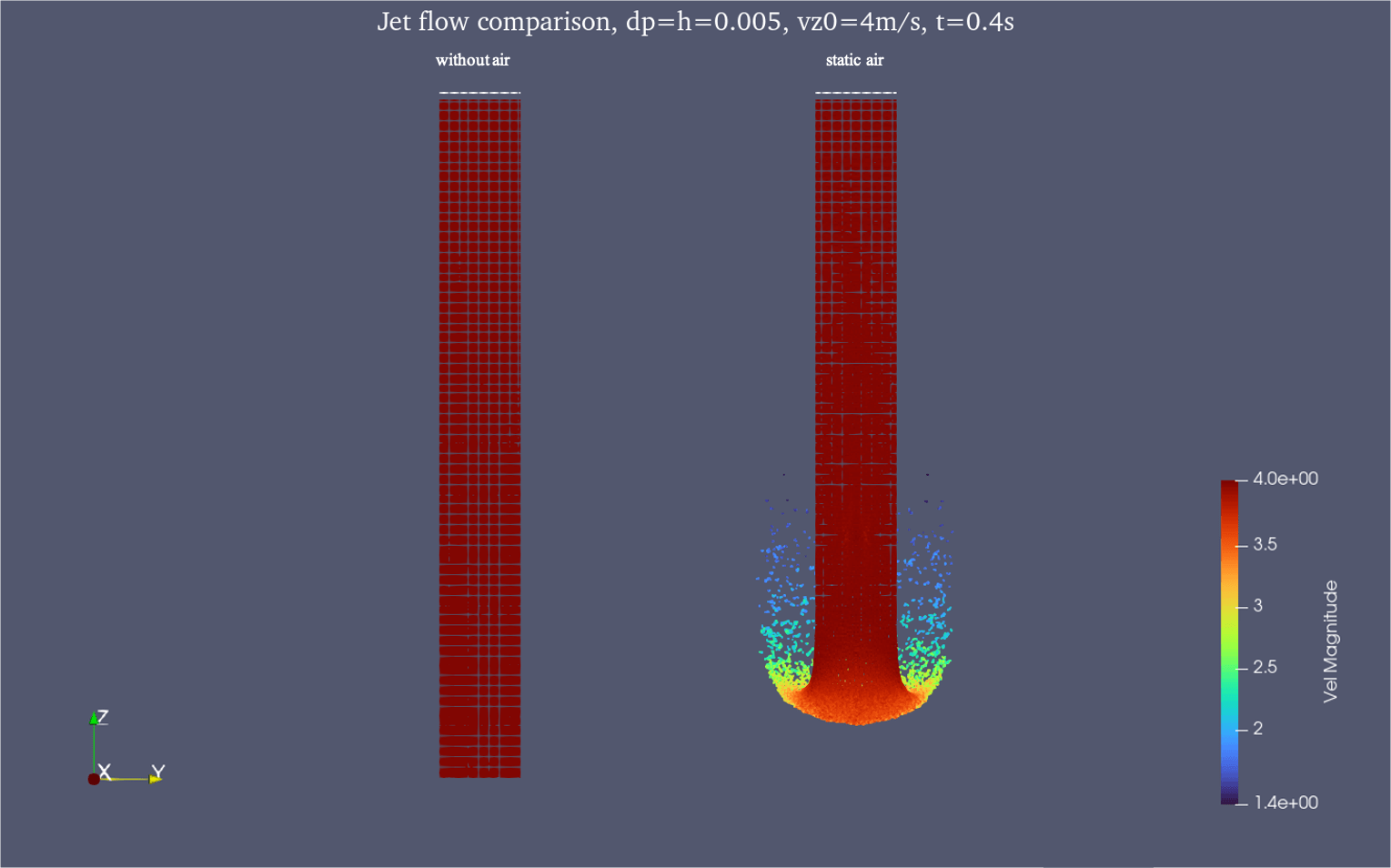Industry-education Cooperation of SAIC-VW and NPU
📍Pre-R&D group, SAIC Volkswagen Automotive Co., Ltd. 🇨🇳
📍School of Software, Northwestern Polytechnical University (Suzhou) 🇨🇳
📍Center of Industrial Software and Complex Fluids Research, Northwestern Polytechnical University (Suzhou) 🇨🇳
📅
05/2022-present👨🏫 Academically supervised by Prof. Zhe JI
Lead developer of team of 4, in charge of algorithm incorporation and code structure design
DualSPHysics,CUDA,C++
Abstract
Through the introduction of new numerical models, the simulation capability of the original open-source Smoothing Length Hydrodynamic software DualSPHysics can be extended to more accurately capture the movement of water affected by factors such as air, material properties of the body surface, and its own material properties, then effectively predict the trajectory of water after rainfall.
This can help the design department to avoid the adverse experience caused by water management failure at the early stage of design, typical scenarios such as trunk raising after rainfall, causing rainwater infiltration into the vehicle and affecting the customer’s experience.
In this work, two key factors are considered to influence the liquid flow on the body surface, namely: surface tension and air drag.
Selected pictures and conclusions
Surface tension
Droplet drops on a plate, calibrate the contact angle $\alpha$ with different configurations:
$\alpha = 60\degree$ | $\alpha = 90\degree$ | $\alpha = 120\degree$ |
Water drop with trunk raising case optimized result:

industral_surface_tension
Air phase
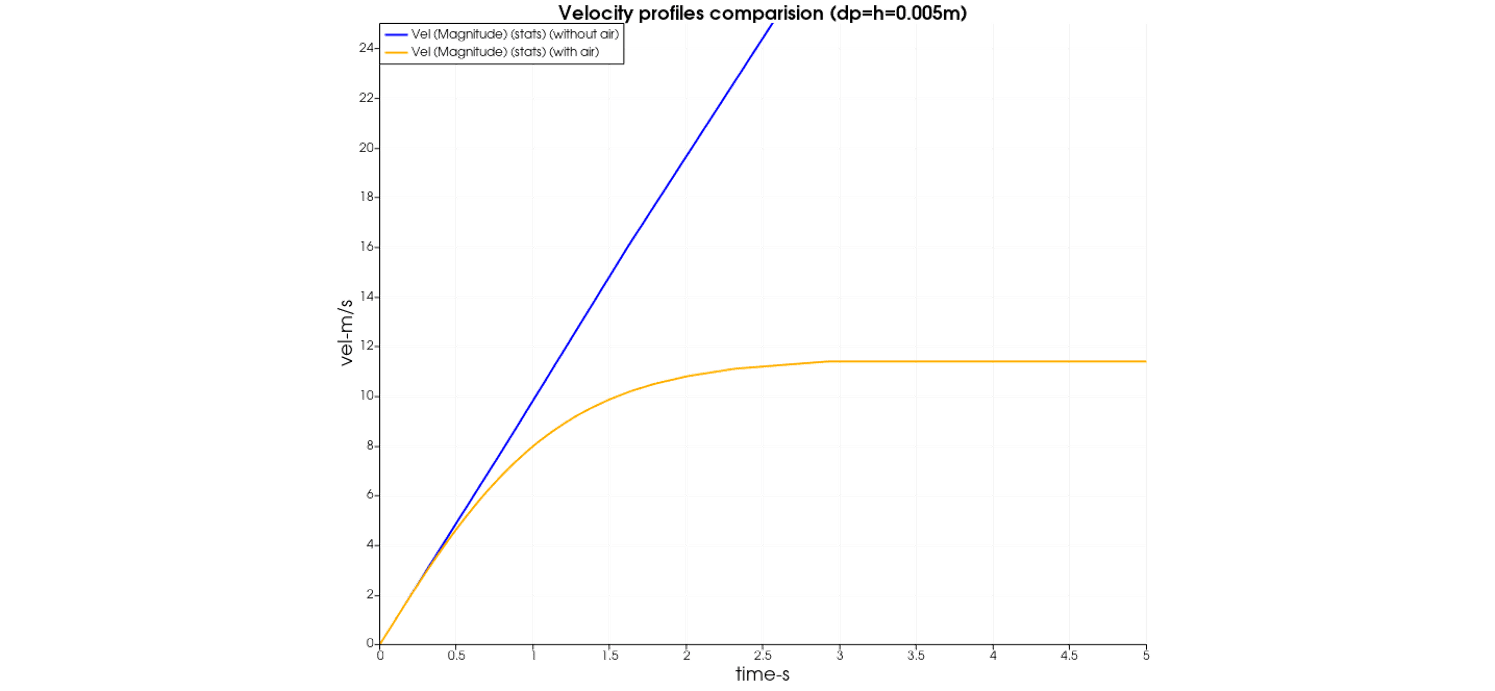
Compare the velocity profiles of a single droplet dropping with and without air phase. And then calibrate the balanced velocity of the with_air scenario:
Compare the results of a jet flow injected into the computational domain with and without air phase: